Offering of Warranties in Colombia: A Guide by the Superintendence of Industry and Commerce
The Superintendence of Industry and Commerce (SIC), the national authority in charge of protecting and guaranteeing free and fair economic competition in Colombia, issued this current year the Offering of Warranties Guide (the Guide), through which it seeks to orient the population on how it approaches the analysis and processing of requests for the offering of warranties, which are aimed to achieve the early termination of investigations for the alleged violation of the free economic competition regime.
In Colombia, the warranties legal concept has existed for approximately 30 years, introduced in the competition protection regime by means of Decree 2153 of 1992, and modified by Law 1340 of 2009. With the passage of time, the application of this concept has varied substantially, from moments of generalized use, to others of reluctance on the part of the SIC to accept the requests of alleged infringers.
Hence, it is possible to establish that the Guide under study is the result of the various interpretations and applications that have been given to the granting of warranties over the years, as it aims to set objective guidelines for those interested in its implementation.
From the outset, it is essential to mention that anticompetitive practices, comprising a series of conducts, such as the subscription of certain agreements or the performance of certain acts, infringe the provisions on the protection of competition by preventing or limiting competition within markets, given that their purpose is to unduly allocate and seize the benefits of a social economy.
Thus, the SIC is in charge of administrative investigations to determine whether there is indeed a violation of the competition protection regime. This procedure, amongst its different phases, contemplates the legal concept of the offering of warranties, which enables the SIC to terminate an administrative investigation in advance in the event that the warranties offered by the alleged infringers, regarding the suspension or modification of the conduct(s) for which they are being investigated, are deemed sufficient. The latter allows the accelerated reestablishment of the market conditions that would have been put at risk, without there being a substantive pronouncement regarding the legality or illegality of such conducts, and without the investigated parties being sanctioned.
All this has the purpose of guaranteeing and safeguarding the welfare and rights of consumers, as well as market performance, while complying with the principles of efficiency and administrative and procedural economy.
Pursuant to the above, the Guide defines the offer of warranties as the "optional request of the alleged infringers containing the granting or offering of warranties for the purpose of suspending or modifying an investigated conduct," which, according to the definition of sufficient warranties, shall be "behavioral and/or structural obligations or commitments of the alleged infringers that meet certain criteria to effectively guarantee the suspension or modification of the conduct under investigation."
Therefore, the acceptance of the offered warranties only proceeds when the SIC deems them sufficient, according to the specific circumstances of each case and the particular conduct, and in consideration of the dynamics of the affected market, to guarantee the effective suspension or modification of the conduct under investigation, to counteract its possible negative effects and to promote free economic competition within the market.
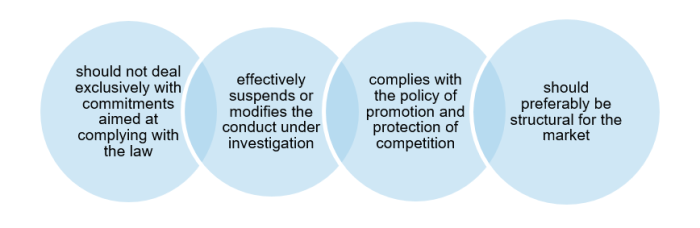
Accordingly, criteria have been developed to serve as a guide to determine when a warranty is sufficient, which, although not limitative, exhaustive or mandatory, are intended to provide general guidance on how the SIC approaches the analysis of requests for the offering of warranties. Thus, the following types of warranty offerings have been accepted:
|
Type |
Behavioral |
Structural |
|
Definition |
commitments aimed at modifying the behavior of alleged offenders within the market |
commitments related to changes or adjustments in the internal corporate structure of the agents under investigation |
|
Example(s) |
1. modify, assign or terminate contracts |
the divestment or sale of assets or the materialization of reforms in the corporate or organizational structure of a market participant |
With respect to behavioral warranties, it is important to mention that these can be divided into internal/external, and positive/negative, as follows:

On the other hand, criteria for the sufficiency of the warranties have been defined, which are neither limitative nor exhaustive, but serve as a guiding parameter for the way in which the SIC approaches and studies the requests for the offer of warranties:
About the Request and Its Processing
The request for warranties must be submitted within 20 working days following the notification of the administrative decree that orders the initiation of the investigation and formulates charges, that is, before the expiration of the term granted to request or provide evidence during the process.
It is important to clarify that the processing of the offering of warranties does not suspend or interrupt the administrative investigation conducted by the SIC.
Now, it is recommended that the offering of warranties:
- is based on truthful, accurate, reliable, verifiable, and suitable information and documentation, avoiding ambiguous offers
- includes a reasonable term for its implementation and materialization
- allows verification of the commitments and obligations acquired by the alleged infringers in the event that, in the opinion of the SIC, substantial changes are evidenced in the conditions of the affected market that may jeopardize the effectiveness of the warranties accepted
- includes collateral warranties that seek to neutralize the possible effects of a breach of the proposed commitments
It is worth mentioning that other investigated parties may support the offering of warranties of an alleged infringer in whole or in part, provided that such manifestation is made within 20 working days following the notification of the administrative decree that orders the initiation of the investigation and formulates charges.
Additionally, and prior to the acceptance or rejection of the request for warranties, the SIC may request clarifications to the alleged infringers regarding their offering and, likewise, to those who have supported them, in order to solicit all the relevant information and/or documentation to establish the content and scope of the proposed and/or supported offerings of warranties. Should the aforementioned happen, and given that the processing of the request allows relative negotiation, the clarifications must be addressed seriously and exhaustively within the term required by the SIC, otherwise the request will be evaluated only in consideration of what was initially established. Hence, it is possible for the interested parties to specify the request and advocate for its acceptance.
Once the proposed warranties have been analyzed, and if the SIC determines that they are sufficient to suspend or modify the conduct under investigation, it will issue an administrative decree through which it will accept the warranty proposal and, consequently, will order the investigation to be filed. In addition, a follow-up scheme of conditions will be established to verify the continuity of compliance with the obligations and commitments acquired, which will be carried out by the Compliance Directorate of the SIC, and may consist of different commitments, such as submitting periodic reports and providing information and/or documents. Regarding the foregoing, it must be taken into consideration that the monitoring activities carried out will be subject to the payment of an annual fee in favor of the SIC.
Failure to comply with the obligations derived from the acceptance of the warranties is thus considered an infringement of the competition protection regulations, and will give rise to the penalties provided by the law, upon request of the explanations required by the SIC.
Should it be found that the warranties offered are not sufficient, for not being considered capable or suitable for the suspension or reform of the conduct, the alleged offenders will be informed of their rejection. However, the decision to reject the offer of warranties does not imply any prejudgment of the conduct under investigation, nor does it generate any sanction for the interested parties.
Lastly, against the decision to accept the offering of warranties, which terminates the administrative investigation in advance, an appeal for reconsideration may be filed before the superintendent of industry and commerce within 10 business days following its notification. However, against the decision not to accept the warranties and not to terminate the investigation in advance, there is no appeal whatsoever.
Information contained in this alert is for the general education and knowledge of our readers. It is not designed to be, and should not be used as, the sole source of information when analyzing and resolving a legal problem, and it should not be substituted for legal advice, which relies on a specific factual analysis. Moreover, the laws of each jurisdiction are different and are constantly changing. This information is not intended to create, and receipt of it does not constitute, an attorney-client relationship. If you have specific questions regarding a particular fact situation, we urge you to consult the authors of this publication, your Holland & Knight representative or other competent legal counsel.